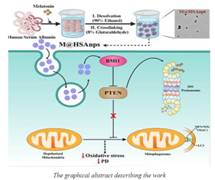
Melatonin, a hormone primarily produced by the pineal gland during the night, is known for its regulatory role in circadian rhythms and sleep cycles. Beyond its endogenous function, melatonin exhibits significant neuroprotective properties, which are crucial in the context of neurodegeneration seen in Parkinson’s disease. Research indicates that melatonin can mitigate oxidative stress, reduce neuroinflammation, and promote neuronal survival, thereby offering a multifaceted approach to combatting the pathophysiology of PD.
The integration of melatonin into nanotechnology presents a promising strategy for enhancing its therapeutic efficacy. Nano-formulation involves encapsulating melatonin in nanoparticles, significantly improving its bioavailability and therapeutic index. This methodology not only allows for sustained release but also facilitates targeted delivery to affected brain regions, thereby maximizing its neuroprotective effect while minimizing systemic side effects.
Moreover, nano-formulated melatonin can enhance the compound’s solubility and stability, which are limitations in its traditional forms. By optimizing these pharmacokinetic properties, the therapeutic potential of melatonin may expand beyond mere symptom relief, possibly modifying disease progression and improving overall patient outcomes.